Cost accountants specialize in analyzing and controlling production costs to enhance cost efficiency and profitability. Management accountants focus on broader financial planning, budgeting, and performance management to support strategic decision-making. Both roles are essential for driving business financial health but differ in scope and emphasis.
Table of Comparison
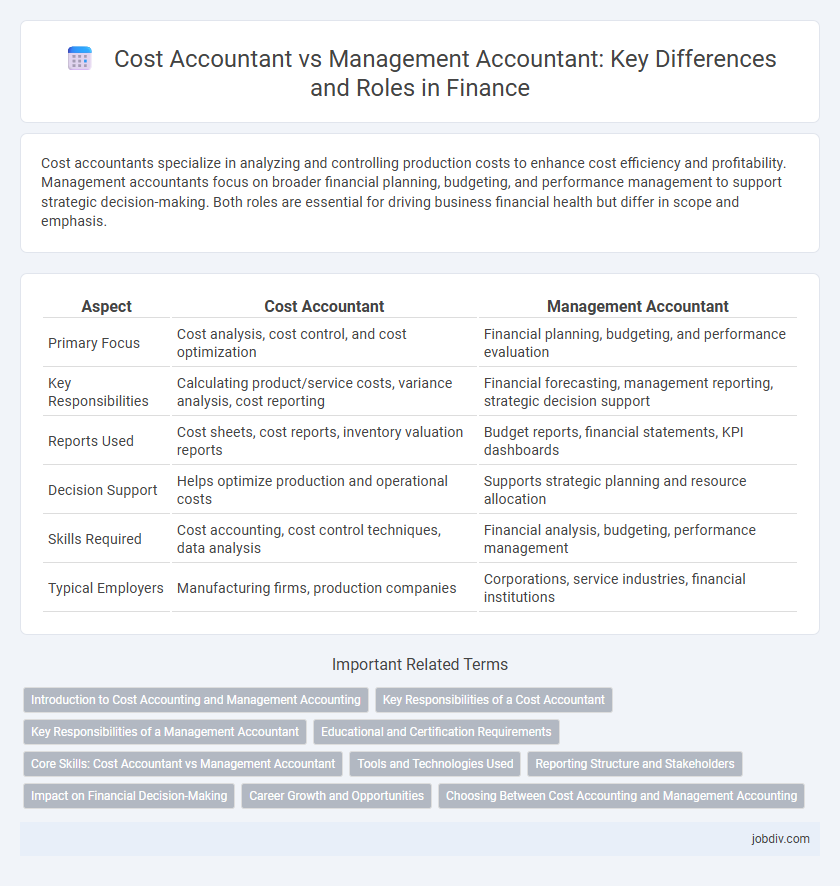
| Aspect | Cost Accountant | Management Accountant |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Cost analysis, cost control, and cost optimization | Financial planning, budgeting, and performance evaluation |
| Key Responsibilities | Calculating product/service costs, variance analysis, cost reporting | Financial forecasting, management reporting, strategic decision support |
| Reports Used | Cost sheets, cost reports, inventory valuation reports | Budget reports, financial statements, KPI dashboards |
| Decision Support | Helps optimize production and operational costs | Supports strategic planning and resource allocation |
| Skills Required | Cost accounting, cost control techniques, data analysis | Financial analysis, budgeting, performance management |
| Typical Employers | Manufacturing firms, production companies | Corporations, service industries, financial institutions |
Introduction to Cost Accounting and Management Accounting
Cost accounting involves recording, analyzing, and controlling direct and indirect costs associated with production to optimize operational efficiency and profitability. Management accounting focuses on providing financial insights and strategic information to support decision-making, planning, and performance management within an organization. Both disciplines utilize budgeting, variance analysis, and cost control but cater to different managerial needs and reporting standards.
Key Responsibilities of a Cost Accountant
Cost Accountants primarily focus on analyzing and controlling costs related to production, budgeting, and inventory valuation to ensure accurate financial reporting. They are responsible for preparing cost sheets, monitoring cost variances, and implementing cost control measures to improve profitability. Their key duties include cost analysis, standard costing, and assisting in pricing decisions based on detailed cost data.
Key Responsibilities of a Management Accountant
Management accountants analyze financial data to support strategic decision-making, budgeting, and forecasting within organizations. They prepare detailed reports on cost control, performance evaluation, and financial planning to guide business operations. Their role involves collaborating with various departments to align financial goals with overall company objectives.
Educational and Certification Requirements
Cost accountants typically require a bachelor's degree in accounting or finance and often pursue certifications like the Certified Management Accountant (CMA) or Certified Cost Accountant (CCA) to specialize in cost analysis and control. Management accountants generally hold degrees in accounting, finance, or business administration and obtain professional credentials such as the CMA or Chartered Management Accountant (ACMA) certification to emphasize strategic financial planning and decision-making. Both roles value continuous education in advanced financial principles, cost management techniques, and regulatory compliance to maintain expertise and professional credibility.
Core Skills: Cost Accountant vs Management Accountant
Cost accountants specialize in cost analysis, budgeting, and inventory valuation, using techniques like standard costing and variance analysis to optimize production expenses. Management accountants focus on financial planning, performance management, and strategic decision-making, employing tools such as budgeting, forecasting, and financial reporting to support business objectives. Both roles require strong analytical skills, proficiency in accounting software, and knowledge of financial regulations, but cost accountants emphasize cost control while management accountants prioritize broader financial strategy.
Tools and Technologies Used
Cost accountants primarily utilize standard costing systems, activity-based costing software, and ERP platforms like SAP and Oracle to analyze and control manufacturing expenses. Management accountants leverage advanced financial modeling tools, business intelligence software such as Tableau and Power BI, and budgeting solutions like Adaptive Insights to support strategic decision-making. Both roles increasingly incorporate automation technologies and data analytics to enhance accuracy and efficiency in financial reporting and cost management.
Reporting Structure and Stakeholders
Cost accountants primarily report to the Finance Manager or Controller, providing detailed cost analysis and budget reports to internal stakeholders such as production managers and operations teams. Management accountants have a broader reporting structure, often presenting financial performance and strategic insights directly to senior executives and board members to support organizational decision-making. Both roles engage with stakeholders, but cost accountants focus more on operational departments while management accountants address a wider range of business units and external parties like investors and regulatory bodies.
Impact on Financial Decision-Making
Cost accountants provide detailed cost analysis and budgeting insights that enable precise product costing and cost control, directly influencing pricing strategies and profitability assessments. Management accountants integrate financial data with strategic planning to support long-term business decisions, risk management, and performance evaluation. Their combined expertise enhances financial decision-making by ensuring both accurate cost management and comprehensive strategic insights.
Career Growth and Opportunities
Cost accountants specialize in budgeting, cost control, and financial reporting, which makes them essential for manufacturing and production sectors aiming for cost efficiency. Management accountants focus on strategic planning, performance management, and decision support, offering broader roles across industries with an emphasis on leadership positions in finance. Career growth for management accountants tends to be faster and more diverse, often leading to CFO roles, while cost accountants typically advance within operational finance teams focusing on process optimization.
Choosing Between Cost Accounting and Management Accounting
Choosing between cost accounting and management accounting depends on the organizational focus; cost accounting emphasizes tracking, recording, and analyzing production costs to aid in budgeting and cost control, while management accounting provides broader financial insights for strategic decision-making, including budgeting, forecasting, and performance evaluation. Cost accountants typically specialize in standardized cost measurement and inventory valuation, whereas management accountants integrate financial and operational data to support managerial planning and strategy. Companies prioritizing precise cost control and product costing may prefer cost accountants, whereas those seeking comprehensive financial analysis for long-term planning benefit more from management accountants.
Cost Accountant vs Management Accountant Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com