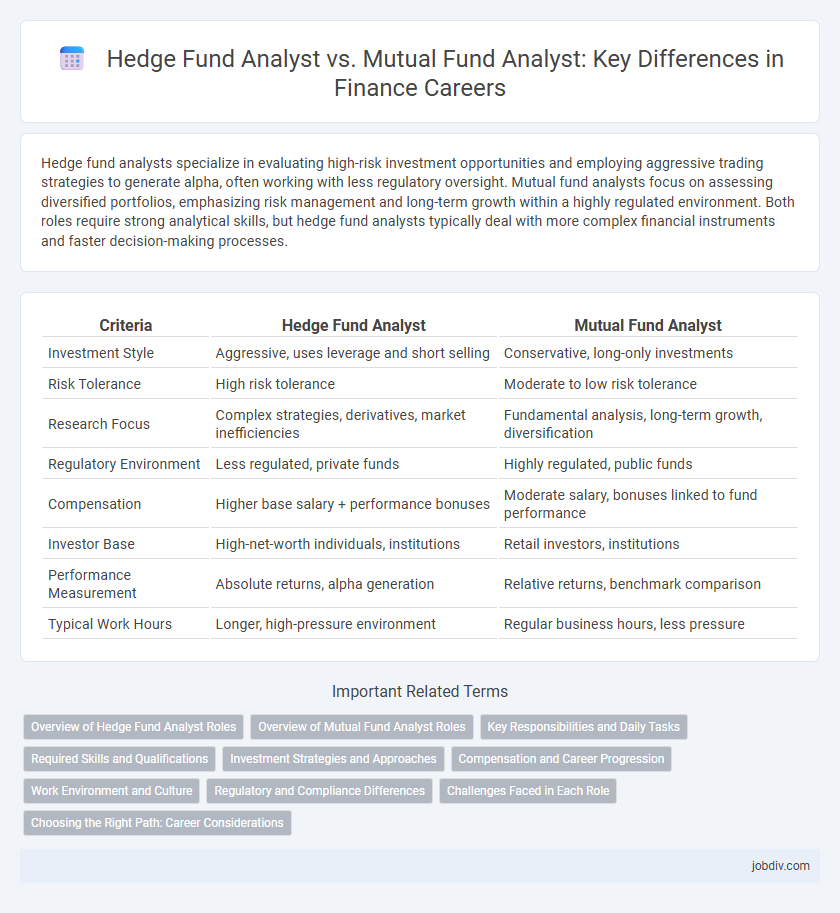
Hedge fund analysts specialize in evaluating high-risk investment opportunities and employing aggressive trading strategies to generate alpha, often working with less regulatory oversight. Mutual fund analysts focus on assessing diversified portfolios, emphasizing risk management and long-term growth within a highly regulated environment. Both roles require strong analytical skills, but hedge fund analysts typically deal with more complex financial instruments and faster decision-making processes.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Hedge Fund Analyst | Mutual Fund Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Style | Aggressive, uses leverage and short selling | Conservative, long-only investments |
| Risk Tolerance | High risk tolerance | Moderate to low risk tolerance |
| Research Focus | Complex strategies, derivatives, market inefficiencies | Fundamental analysis, long-term growth, diversification |
| Regulatory Environment | Less regulated, private funds | Highly regulated, public funds |
| Compensation | Higher base salary + performance bonuses | Moderate salary, bonuses linked to fund performance |
| Investor Base | High-net-worth individuals, institutions | Retail investors, institutions |
| Performance Measurement | Absolute returns, alpha generation | Relative returns, benchmark comparison |
| Typical Work Hours | Longer, high-pressure environment | Regular business hours, less pressure |
Overview of Hedge Fund Analyst Roles
Hedge fund analysts conduct in-depth research to identify high-return investment opportunities across diverse asset classes, employing advanced financial modeling and risk assessment techniques. They monitor market trends, analyze economic data, and evaluate complex securities to generate alpha within aggressive investment strategies. These analysts often collaborate with portfolio managers to optimize hedge fund performance under dynamic market conditions.
Overview of Mutual Fund Analyst Roles
Mutual Fund Analysts evaluate and monitor the performance of mutual funds, analyzing portfolio holdings, market trends, and financial statements to provide investment recommendations. They focus on assessing risk, asset allocation, and fund managers' strategies to enhance returns for retail and institutional investors. Their role involves extensive quantitative analysis and reporting to support fund managers in maintaining compliance with regulatory standards and achieving fund objectives.
Key Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
Hedge fund analysts specialize in evaluating complex investment strategies, conducting in-depth market research, and identifying high-risk, high-reward opportunities to maximize portfolio returns. Mutual fund analysts focus on assessing diversified asset classes, analyzing economic trends, and monitoring fund performance to ensure consistent, long-term growth aligned with investor objectives. Both roles require robust financial modeling and data analysis, but hedge fund analysts emphasize short-term gains while mutual fund analysts prioritize risk management and steady returns.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Hedge fund analysts require advanced quantitative skills, proficiency in financial modeling, and expertise in alternative investment strategies to manage complex portfolios and assess risk exposure effectively. Mutual fund analysts focus on fundamental analysis, strong understanding of equity and fixed-income securities, and regulatory compliance knowledge to evaluate long-term investment opportunities and align with investor goals. Both roles demand strong analytical abilities, CFA certification is highly valued, and excellent communication skills are essential for presenting findings to portfolio managers and clients.
Investment Strategies and Approaches
Hedge fund analysts employ aggressive investment strategies, including leveraging, short selling, and derivatives, to achieve high returns with elevated risk profiles. Mutual fund analysts focus on diversified portfolios with long-only positions, emphasizing risk management and steady growth aligned with investor objectives. The hedge fund analyst's approach is typically opportunistic and flexible, while the mutual fund analyst prioritizes regulatory compliance and consistent performance.
Compensation and Career Progression
Hedge fund analysts typically earn higher base salaries and performance-based bonuses compared to mutual fund analysts due to the high-risk, high-reward nature of hedge fund strategies. Career progression for hedge fund analysts often involves faster advancement to portfolio manager roles, driven by direct contributions to fund performance, whereas mutual fund analysts may experience steadier, more structured growth within large asset management firms. Compensation in hedge funds can vary widely based on fund size and success, while mutual fund analysts benefit from more predictable salaries and bonuses aligned with long-term fund performance.
Work Environment and Culture
Hedge fund analysts typically work in high-pressure, fast-paced environments that emphasize agility, innovation, and aggressive risk-taking, often within smaller teams and more exclusive firms. Mutual fund analysts enjoy a more structured, regulated, and collaborative setting, where long-term growth and risk management align with broader investor protection standards. Culture in hedge funds tends to reward performance-driven results and entrepreneurial thinking, whereas mutual funds prioritize stability, compliance, and fiduciary responsibility.
Regulatory and Compliance Differences
Hedge fund analysts operate under less stringent regulatory frameworks compared to mutual fund analysts, as hedge funds are typically governed by the Investment Advisers Act of 1940 with exemptions, leading to fewer disclosure requirements. Mutual fund analysts must comply with the Investment Company Act of 1940, which mandates extensive transparency, regular reporting, and strict adherence to investor protection regulations. These regulatory differences impact the scope of compliance monitoring, risk assessment protocols, and reporting obligations inherent to each analyst's role.
Challenges Faced in Each Role
Hedge fund analysts confront challenges such as handling high-risk, high-reward investment strategies and performing extensive due diligence on complex, often illiquid assets within a fast-paced environment. Mutual fund analysts face regulatory constraints and the pressure to achieve consistent, long-term returns by meticulously analyzing diversified portfolios and managing client expectations. Both roles require strong quantitative skills, but hedge fund analysts must adapt quickly to volatile markets, while mutual fund analysts focus on stability and compliance.
Choosing the Right Path: Career Considerations
Hedge fund analysts typically focus on complex strategies, high-risk investments, and performance-driven environments, demanding strong quantitative skills and adaptability to market volatility. Mutual fund analysts prioritize long-term value investing, portfolio diversification, and regulatory compliance, appealing to those interested in stable growth and client-focused outcomes. Choosing the right path depends on your risk tolerance, investment strategy preference, and desired work environment within the finance industry.
Hedge Fund Analyst vs Mutual Fund Analyst Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com