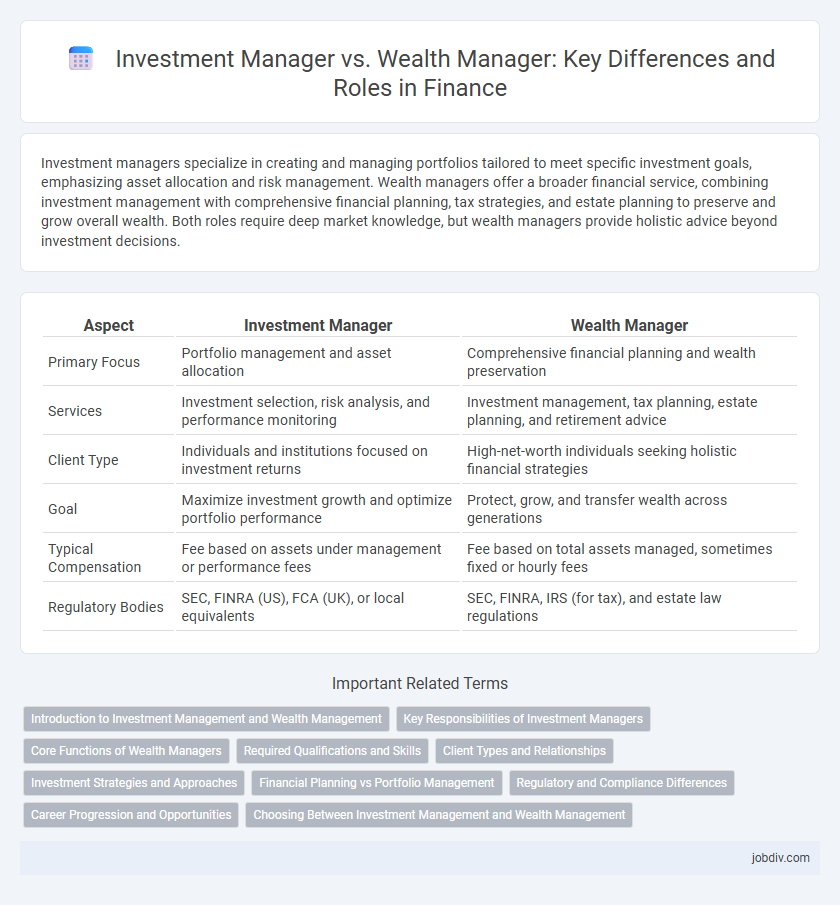
Investment managers specialize in creating and managing portfolios tailored to meet specific investment goals, emphasizing asset allocation and risk management. Wealth managers offer a broader financial service, combining investment management with comprehensive financial planning, tax strategies, and estate planning to preserve and grow overall wealth. Both roles require deep market knowledge, but wealth managers provide holistic advice beyond investment decisions.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Investment Manager | Wealth Manager |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Portfolio management and asset allocation | Comprehensive financial planning and wealth preservation |
| Services | Investment selection, risk analysis, and performance monitoring | Investment management, tax planning, estate planning, and retirement advice |
| Client Type | Individuals and institutions focused on investment returns | High-net-worth individuals seeking holistic financial strategies |
| Goal | Maximize investment growth and optimize portfolio performance | Protect, grow, and transfer wealth across generations |
| Typical Compensation | Fee based on assets under management or performance fees | Fee based on total assets managed, sometimes fixed or hourly fees |
| Regulatory Bodies | SEC, FINRA (US), FCA (UK), or local equivalents | SEC, FINRA, IRS (for tax), and estate law regulations |
Introduction to Investment Management and Wealth Management
Investment management involves the professional handling of financial assets and securities to achieve specific growth or income objectives, emphasizing portfolio diversification, risk assessment, and market analysis. Wealth management integrates comprehensive financial planning, including investment management, tax strategies, estate planning, and retirement solutions tailored to high-net-worth individuals. Both disciplines require expertise in asset allocation but diverge in scope, with investment managers focusing primarily on investment portfolios and wealth managers addressing broader financial goals and legacy preservation.
Key Responsibilities of Investment Managers
Investment managers primarily focus on constructing and managing investment portfolios by conducting thorough market analysis, selecting appropriate assets, and executing trades to maximize client returns. They continuously monitor portfolio performance and adjust strategies based on market conditions, risk tolerance, and financial goals. Investment managers also provide detailed reporting and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements to protect client interests.
Core Functions of Wealth Managers
Wealth managers specialize in comprehensive financial planning, estate planning, tax optimization, and personalized investment strategies tailored to high-net-worth clients. They coordinate various financial services, including trust management and retirement planning, to preserve and grow client wealth over the long term. Unlike investment managers who primarily focus on portfolio management, wealth managers deliver holistic financial solutions integrating multiple aspects of a client's financial life.
Required Qualifications and Skills
Investment managers typically require certifications such as the Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) designation, strong analytical skills, and expertise in portfolio management and market analysis. Wealth managers often hold Certified Financial Planner (CFP) credentials and excel in holistic financial planning, tax strategies, and client relationship management. Both roles demand deep financial knowledge, but investment managers emphasize asset allocation and risk assessment, while wealth managers focus on personalized wealth growth and preservation strategies.
Client Types and Relationships
Investment managers primarily serve institutional clients and high-net-worth individuals, focusing on portfolio management and asset allocation to maximize returns. Wealth managers provide a broader range of financial services, including estate planning, tax advice, and retirement planning, catering to affluent individuals and families. Client relationships for investment managers tend to be more transactional and investment-specific, while wealth managers build long-term, holistic financial partnerships.
Investment Strategies and Approaches
Investment managers primarily focus on selecting and managing a diversified portfolio of assets to achieve specific financial goals, using quantitative analysis and market research to optimize returns. Wealth managers provide a holistic approach that integrates investment strategies with financial planning, tax optimization, estate planning, and risk management to preserve and grow overall client wealth. While investment managers emphasize active or passive asset allocation, wealth managers tailor investment approaches to align with clients' broader financial objectives and life circumstances.
Financial Planning vs Portfolio Management
Investment managers specialize in portfolio management, focusing on selecting and overseeing a diverse range of assets to maximize returns and manage risk within client portfolios. Wealth managers provide comprehensive financial planning services that include retirement strategies, tax optimization, estate planning, and cash flow management, addressing the broader financial goals of high-net-worth individuals. While investment managers concentrate primarily on asset allocation and market performance, wealth managers integrate these strategies into a holistic plan tailored to the client's long-term financial well-being.
Regulatory and Compliance Differences
Investment managers primarily adhere to regulations such as the Investment Advisers Act of 1940, emphasizing fiduciary duties and portfolio management compliance, while wealth managers must comply with broader financial regulations including anti-money laundering (AML) laws and estate planning rules. Wealth managers often navigate complex trust and tax laws, requiring specialized compliance protocols beyond those of investment managers. Regulatory bodies like the SEC oversee investment managers more directly, whereas wealth managers may face oversight from multiple agencies due to their diverse service offerings.
Career Progression and Opportunities
Investment managers typically focus on portfolio management and asset allocation, advancing through roles such as analyst, portfolio manager, and chief investment officer, with opportunities in hedge funds, mutual funds, and private equity firms. Wealth managers provide holistic financial planning, estate, and tax advisory for high-net-worth clients, often progressing to senior advisor and partner roles within private banks or advisory firms. Both careers offer lucrative opportunities, but wealth management emphasizes client relationship building, while investment management centers on market analysis and investment strategy.
Choosing Between Investment Management and Wealth Management
Investment managers specialize in managing investment portfolios, focusing on asset allocation, risk assessment, and maximizing returns through market opportunities. Wealth managers provide comprehensive financial planning, including estate planning, tax strategies, retirement planning, and investment advice tailored to high-net-worth individuals. Choosing between the two depends on your financial goals: prioritize pure investment growth with an investment manager or holistic financial well-being with a wealth manager.
Investment Manager vs Wealth Manager Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com