Brokers provide independent advice and work with multiple insurance companies to find the best coverage tailored to the client's needs, while agents typically represent one insurer and offer policies from that specific company. Brokers are legally obligated to act in the best interest of their clients, ensuring personalized service and unbiased recommendations. Agents focus on selling products from their associated insurer, which may limit options but can offer specialized expertise in those policies.
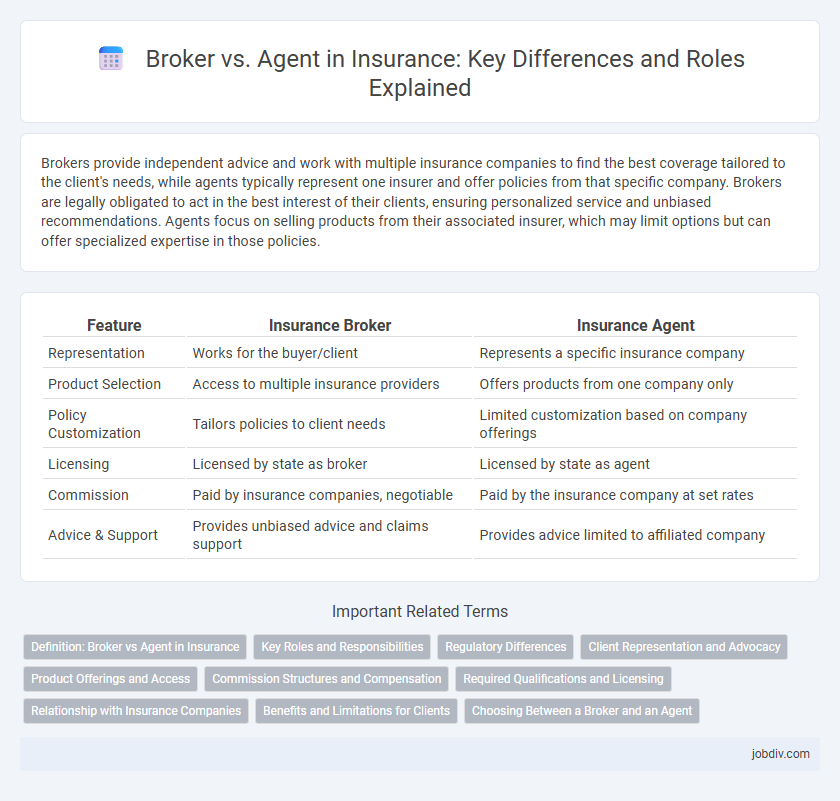
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Insurance Broker | Insurance Agent |
|---|---|---|
| Representation | Works for the buyer/client | Represents a specific insurance company |
| Product Selection | Access to multiple insurance providers | Offers products from one company only |
| Policy Customization | Tailors policies to client needs | Limited customization based on company offerings |
| Licensing | Licensed by state as broker | Licensed by state as agent |
| Commission | Paid by insurance companies, negotiable | Paid by the insurance company at set rates |
| Advice & Support | Provides unbiased advice and claims support | Provides advice limited to affiliated company |
Definition: Broker vs Agent in Insurance
An insurance broker acts as an independent intermediary representing multiple insurance companies, offering clients a variety of policy options tailored to their specific needs. In contrast, an insurance agent typically works on behalf of a single insurer, providing products and services exclusively from that company. Brokers prioritize client interests by comparing coverage terms and prices, whereas agents focus on selling and servicing policies from one insurer.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
A broker acts as an intermediary between clients and multiple insurance companies, offering unbiased advice to find the best policy tailored to the client's needs, while agents represent one or more specific insurers and focus on selling their company's products. Brokers conduct thorough market research to compare policies and negotiate terms on behalf of clients, whereas agents provide detailed information, policy quotes, and assist with claims within the framework of their insurer's offerings. Both play critical roles in risk management, but brokers prioritize client interests with a broader market perspective, whereas agents emphasize product expertise and insurer-specific solutions.
Regulatory Differences
Insurance brokers operate independently and are regulated to act in the best interest of their clients, offering a wider range of insurance products from multiple providers. Agents are typically affiliated with one or more insurance companies and are regulated to represent those companies' products, often with a more limited selection. Regulatory bodies require brokers to adhere to fiduciary duties, while agents must comply with company-specific guidelines and licensing requirements in each jurisdiction.
Client Representation and Advocacy
A broker acts as an independent representative who advocates for the client's best interests by comparing multiple insurance providers and policies to find tailored coverage solutions. In contrast, an agent typically represents one or more specific insurance companies, prioritizing the insurer's products and interests. Brokers provide unbiased advice and personalized client advocacy, ensuring optimal protection aligned with individual needs and risk profiles.
Product Offerings and Access
Insurance brokers offer access to multiple insurance carriers, providing a wide range of product offerings tailored to diverse client needs. Agents typically represent one or a limited number of insurers, which can restrict product variety but ensures specialized knowledge of those specific offerings. Brokers' broader market access enables personalized comparisons, while agents may offer streamlined service with focused expertise.
Commission Structures and Compensation
Commission structures significantly differ between insurance brokers and agents, impacting their compensation models. Brokers typically earn commissions from multiple insurance companies based on the policies they place with various insurers, allowing them a broader range of income opportunities. Conversely, agents usually receive commissions from a single insurance company, often tied to specific products, with additional bonuses linked to sales targets and policy renewals.
Required Qualifications and Licensing
Insurance brokers require a state license that mandates passing a comprehensive exam covering various insurance products and regulations, ensuring they can advise clients independently. Agents must also obtain a state-issued license specific to the insurance lines they sell, often necessitating pre-licensing education and ongoing continuing education to maintain compliance. Licensing authorities like state insurance departments enforce strict qualification standards, emphasizing knowledge, ethical conduct, and client protection for both brokers and agents.
Relationship with Insurance Companies
Insurance brokers act as intermediaries representing clients and work with multiple insurance companies to find the best coverage options. Agents typically represent one insurance company, offering products and services specific to that insurer. Brokers have a broader range of insurance providers to choose from, while agents maintain a closer, exclusive relationship with their insurance company.
Benefits and Limitations for Clients
Insurance brokers offer clients access to multiple insurance carriers, enabling tailored policy comparisons and competitive pricing, while agents typically represent one insurer, providing specialized knowledge of that company's products. Brokers benefit clients by advocating for their interests and facilitating customized coverage, but limitations include potentially higher fees and less direct insurer support. Agents provide streamlined service and quicker claims processing due to their close insurer relationships, though clients may face restricted options and less impartial advice.
Choosing Between a Broker and an Agent
Choosing between an insurance broker and an agent depends on your need for personalized coverage options versus exclusive carrier representation. Brokers offer access to multiple insurers, providing unbiased advice and comparing a wide range of policies to find the best fit. Agents typically represent one or more specific insurance companies, delivering expertise in those providers' products and streamlined service.
Broker vs Agent Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com