Captive managers specialize in administering insurance companies owned by the insureds, providing tailored risk management and compliance services that align with the parent organization's specific requirements. In contrast, Managing General Agents (MGAs) act as intermediaries empowered by insurers to underwrite policies, handle claims, and manage distribution channels, offering flexibility and market reach without ownership of the insurance entity. Understanding the distinctions between captive managers and MGAs is crucial for businesses seeking optimal control, risk retention, and operational efficiency in their insurance strategies.
Table of Comparison
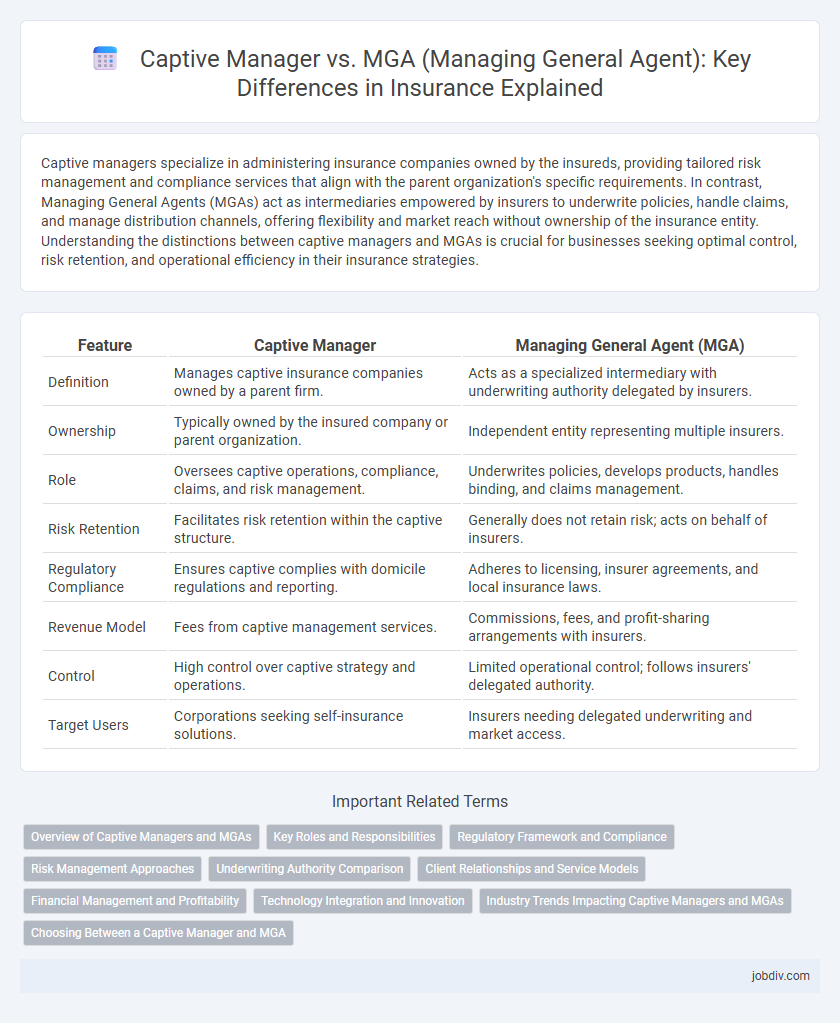
| Feature | Captive Manager | Managing General Agent (MGA) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manages captive insurance companies owned by a parent firm. | Acts as a specialized intermediary with underwriting authority delegated by insurers. |
| Ownership | Typically owned by the insured company or parent organization. | Independent entity representing multiple insurers. |
| Role | Oversees captive operations, compliance, claims, and risk management. | Underwrites policies, develops products, handles binding, and claims management. |
| Risk Retention | Facilitates risk retention within the captive structure. | Generally does not retain risk; acts on behalf of insurers. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Ensures captive complies with domicile regulations and reporting. | Adheres to licensing, insurer agreements, and local insurance laws. |
| Revenue Model | Fees from captive management services. | Commissions, fees, and profit-sharing arrangements with insurers. |
| Control | High control over captive strategy and operations. | Limited operational control; follows insurers' delegated authority. |
| Target Users | Corporations seeking self-insurance solutions. | Insurers needing delegated underwriting and market access. |
Overview of Captive Managers and MGAs
Captive Managers specialize in administering captive insurance companies, providing services such as regulatory compliance, risk management, and financial oversight tailored to the parent company's unique risk profile. Managing General Agents (MGAs) operate as intermediaries between insurers and agents, underwriting policies, managing claims, and providing customized insurance solutions with delegated authority from insurers. Both entities enhance operational efficiency but differ significantly in scope, with Captive Managers focusing on captive insurance entities and MGAs on broader market-facing distribution and underwriting functions.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
Captive Managers oversee the establishment, administration, and regulatory compliance of captive insurance companies, ensuring risk management and financial reporting align with the parent company's objectives. Managing General Agents (MGAs) handle underwriting, policy issuance, and claims processing on behalf of insurers, leveraging specialized expertise to expand market reach and improve customer service. While Captive Managers focus on captive ownership and risk retention strategies, MGAs concentrate on operational functions and underwriting authority within delegated authority agreements.
Regulatory Framework and Compliance
The regulatory framework for Captive Managers involves stringent compliance with domicile-specific captive insurance laws, including regular financial reporting, risk management assessments, and adherence to solvency requirements. Managing General Agents (MGAs) operate under broader insurance regulations dictated by the states or countries where they are licensed, requiring them to maintain licenses, comply with underwriting guidelines, and meet specific consumer protection standards. Compliance responsibilities for Captive Managers are more focused on internal risk control and policyholder protections within the captive structure, while MGAs must continuously align with market conduct rules and insurance carrier mandates.
Risk Management Approaches
Captive managers primarily focus on tailoring risk management strategies to suit the specific needs of the parent company, emphasizing loss control, claims handling, and regulatory compliance within the captive insurance framework. MGAs adopt a more diversified risk management approach, underwriting and managing insurance policies across multiple carriers while leveraging technology and data analytics to optimize risk selection and pricing. Both roles play critical roles in mitigating insurance risks, but captive managers operate within a self-insurance model, whereas MGAs act as intermediaries with delegated underwriting authority.
Underwriting Authority Comparison
Captive Managers hold underwriting authority exclusively within the captive insurance company they manage, enabling tailored risk assessments aligned with the parent organization's risk profile. MGAs possess delegated underwriting authority from one or multiple insurers, allowing them to underwrite policies and bind coverage on behalf of these insurers across various markets. The scope of underwriting authority for MGAs is generally broader but subject to insurer-imposed limits, whereas Captive Managers operate with full authority constrained to their captive's strategic risk parameters.
Client Relationships and Service Models
Captive Managers specialize in tailored risk management solutions for parent companies, offering direct control over policy administration and underwriting, which fosters deep, long-term client relationships through personalized service models. Managing General Agents (MGAs) operate with delegated authority from insurers, managing multiple carriers and providing flexible, scalable services that emphasize efficient client onboarding and diverse product offerings. The service model of Captive Managers tends to be highly customized and collaborative, while MGAs prioritize agility and broad market access to meet varied client needs.
Financial Management and Profitability
Captive managers specialize in overseeing the financial operations of captive insurance companies, ensuring risk retention strategies optimize capital allocation and enhance profitability by controlling underwriting expenses. MGAs operate as intermediaries with delegated underwriting authority, focusing on maximizing profitability through commissions and efficient policy management while managing risk portfolios for insurers. The key financial distinction lies in captive managers driving internal cost efficiencies and risk retention benefits, whereas MGAs leverage market expertise and distribution channels to enhance revenue streams and profitability.
Technology Integration and Innovation
Captive Managers leverage advanced technology platforms to streamline risk management and enhance transparency for insurance-controlled entities, often integrating bespoke analytics and automation tools tailored to captive insurance structures. MGAs prioritize scalable digital solutions and InsurTech innovations to optimize underwriting, policy administration, and claims processing, enabling faster market responsiveness and improved customer engagement. Both entities invest in AI-driven data analytics and cloud-based systems, but Captive Managers focus on customizable risk control technologies, while MGAs emphasize broad digital distribution and operational efficiency.
Industry Trends Impacting Captive Managers and MGAs
Industry trends such as increased regulatory scrutiny and the rise of insurtech innovations are reshaping the roles of Captive Managers and MGAs, pushing for enhanced compliance and technology adoption. Captive Managers are increasingly leveraging data analytics and risk management tools to optimize captive insurance structures, while MGAs focus on agile underwriting platforms and digital distribution channels to expand market reach. The growing demand for tailored insurance products and faster claims processing drives both entities to integrate AI and automation, fundamentally transforming operational efficiency and customer engagement.
Choosing Between a Captive Manager and MGA
Selecting between a Captive Manager and an MGA hinges on control and operational focus within insurance management. Captive Managers primarily handle risk retention and custom policy administration for the parent company, ensuring tailored coverage and financial oversight. MGAs offer broader underwriting authority and market access, specializing in niche markets and leveraging extensive carrier relationships to optimize underwriting and distribution.
Captive Manager vs MGA (Managing General Agent) Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com