Risk analysts evaluate potential hazards and quantify financial exposure by analyzing data to develop strategies that minimize insurance claims. Loss control specialists implement practical safety measures and inspections to reduce the frequency and severity of losses before they occur. While risk analysts focus on forecasting and planning, loss control specialists concentrate on operational prevention and safety compliance.
Table of Comparison
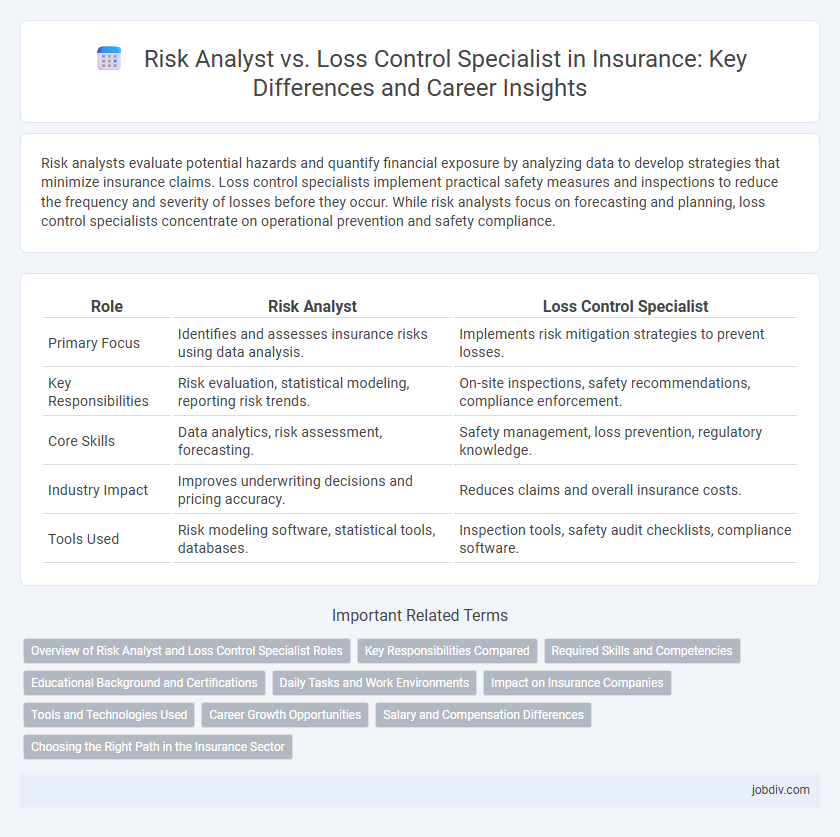
| Role | Risk Analyst | Loss Control Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Identifies and assesses insurance risks using data analysis. | Implements risk mitigation strategies to prevent losses. |
| Key Responsibilities | Risk evaluation, statistical modeling, reporting risk trends. | On-site inspections, safety recommendations, compliance enforcement. |
| Core Skills | Data analytics, risk assessment, forecasting. | Safety management, loss prevention, regulatory knowledge. |
| Industry Impact | Improves underwriting decisions and pricing accuracy. | Reduces claims and overall insurance costs. |
| Tools Used | Risk modeling software, statistical tools, databases. | Inspection tools, safety audit checklists, compliance software. |
Overview of Risk Analyst and Loss Control Specialist Roles
Risk Analysts evaluate potential financial risks by analyzing data trends and probability models to develop strategies that minimize exposure for insurance companies. Loss Control Specialists focus on identifying, assessing, and mitigating physical hazards in insured properties or operations to prevent accidents and losses. Both roles collaborate to enhance risk management processes, ensuring comprehensive protection and cost reduction for insurers and clients.
Key Responsibilities Compared
Risk Analysts evaluate insurance applications by analyzing financial documents and historical claims data to assess potential risks and determine policy terms. Loss Control Specialists focus on mitigating risks through site inspections, safety audits, and recommending risk reduction strategies directly to clients. While Risk Analysts prioritize risk assessment and pricing, Loss Control Specialists emphasize proactive loss prevention and compliance with safety regulations.
Required Skills and Competencies
Risk Analysts require strong analytical skills, proficiency in data interpretation, and expertise in statistical modeling to assess potential insurance risks accurately. Loss Control Specialists need practical knowledge of safety regulations, excellent communication abilities, and experience in implementing risk mitigation strategies to prevent losses. Both roles demand attention to detail and a thorough understanding of industry standards to optimize insurance outcomes effectively.
Educational Background and Certifications
Risk Analysts typically hold degrees in finance, economics, or statistics, with certifications such as the Chartered Enterprise Risk Analyst (CERA) enhancing their expertise in quantitative risk assessment. Loss Control Specialists often possess backgrounds in engineering, safety management, or occupational health, and certifications like the Associate in Risk Management (ARM) or Certified Safety Professional (CSP) demonstrate proficiency in identifying and mitigating physical risks. Both roles value continuous education, but Risk Analysts prioritize analytical credentials while Loss Control Specialists focus on practical safety certifications.
Daily Tasks and Work Environments
Risk Analysts evaluate data and trends to identify potential risks and recommend strategies to mitigate financial loss, primarily working in office settings with extensive use of statistical software and risk modeling tools. Loss Control Specialists conduct on-site inspections to assess workplace safety, recommend improvements to reduce hazards, and collaborate directly with clients across various industries, often spending significant time in the field. Both roles aim to minimize insurance claims but differ in their focus--Risk Analysts emphasize data analysis and forecasting, while Loss Control Specialists prioritize hands-on safety evaluation and prevention.
Impact on Insurance Companies
Risk analysts assess and quantify potential financial losses by analyzing data and trends, enabling insurance companies to price policies accurately and maintain profitability. Loss control specialists implement risk mitigation strategies and safety programs that reduce the frequency and severity of claims, directly lowering underwriting expenses. Together, these roles optimize risk management, enhance policyholder safety, and improve overall financial stability for insurers.
Tools and Technologies Used
Risk Analysts utilize advanced data analytics software, predictive modeling tools, and risk assessment platforms to evaluate potential exposures and forecast future losses. Loss Control Specialists rely on inspection technologies, safety management systems, and real-time monitoring devices to identify hazards and implement preventive measures. Both roles increasingly incorporate artificial intelligence, geographic information systems (GIS), and cloud-based applications to enhance accuracy and efficiency in risk mitigation.
Career Growth Opportunities
Risk Analysts typically experience accelerated career growth by leveraging advanced data analytics and predictive modeling to assess potential insurance losses, making them vital in underwriting and strategic decision-making roles. Loss Control Specialists often transition into senior risk management or safety consultancy positions, applying hands-on expertise in hazard identification and mitigation to reduce claims and improve workplace safety. Both roles offer distinct career trajectories: Risk Analysts move towards data-driven leadership in risk assessment, while Loss Control Specialists advance through practical risk reduction and compliance management.
Salary and Compensation Differences
Risk Analysts typically earn an average salary ranging from $65,000 to $95,000 annually, reflecting their role in assessing and quantifying potential financial risks. Loss Control Specialists, focused on minimizing insurance claims through proactive risk mitigation, generally receive compensation between $55,000 and $85,000 per year. Bonuses and incentive pay are more prevalent for Risk Analysts due to their direct impact on underwriting decisions and portfolio risk management.
Choosing the Right Path in the Insurance Sector
Risk analysts specialize in assessing potential financial uncertainties by utilizing statistical models and data analysis to predict losses, guiding underwriting and investment decisions. Loss control specialists focus on implementing safety measures and risk mitigation strategies on-site to prevent accidents and minimize claims, directly influencing operational risk management. Selecting the right path depends on whether an individual prefers analytical roles centered on data-driven risk evaluation or hands-on positions aimed at proactive hazard reduction within the insurance industry.
Risk Analyst vs Loss Control Specialist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com